Book Online
You Can Request Appointment(Pending Confirmation) in 24 Hours
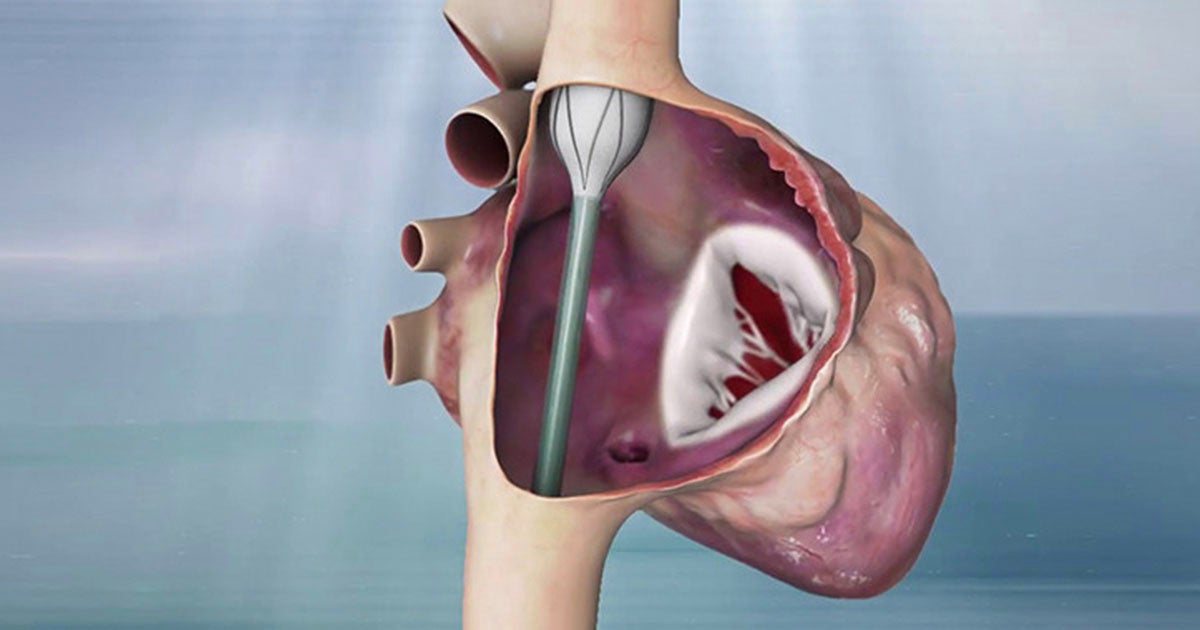
Tricuspid regurgitation evaluation and pre-procedural planning TTVR requires accurate evaluation of the TV apparatus (with a particular focus on the TV annulus) and of the RV.
Echocardiography plays a major role, allowing complete assessment of the TV as well as RV pathophysiology. Since the TV is the most anterior structure of the heart, transthoracic 2D and 3D are fundamental and usually offer good imaging due to low thoracic impedance. It allows good evaluation of TR severity and etiology, as well as RV function and pulmonary pressure. Transesophageal echo (TEE), especially with full 3D sets, may help define the mechanism of TR and morphologically characterize the TV: detailed assessment of tricuspid leaflet morphology and function can be obtained, as well as TV annulus dimensions and function.
Computed tomography imaging, with multiplanar 3-dimensional reconstruction, is essential for preprocedural TV structural evaluation. It allows precise measurement of the RV dimensions and TV annulus size, its relation with the right coronary artery, and the distance between the TV annulus and RV apex. In addition, CT enables preprocedural fluoroscopic angulation calculation and assessment of the access site dimensions and course (e.g. subclavian and axillary veins) for TTVR (25). However, CT exposes patients to iodinated contrast media, which need to be considered during procedural planning in those patients with impaired renal function.
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging can be utilized as an adjunctive imaging modality for TV assessment prior to TTVR. It can be used for anatomical and functional assessment due to its excellent spatial resolution. CMR imaging with dedicated RV planes provides detailed RV chamber evaluation that is comparable to 3-dimensional echocardiography; however, unlike echocardiography it is not hampered by the patient’s body habitus or lung fields. In addition, for patients with atrial tachycardias or fibrillation, free-breathing CMR sequencing is effective in providing quantitative evaluation.
CMR evaluation of TV leaflet morphology can be challenging because of the thin nature of the leaflets. Evaluation of the TV annulus can be performed using breath-held cine using multiple long-axis views. Moreover, offline multiplane reconstruction can be performed to get detailed anatomical evaluation of the TV annulus. Lastly, severity of TR can be calculated using indirect quantification (difference between the planimetered RV stroke volume and forward pulmonic flow volume)